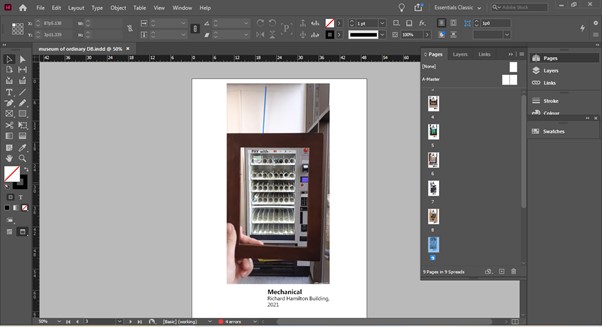
We began this week’s lecture, by reading the beginning of the book Ways of Seeing by John Berger. I have read the book earlier in the week but found it far more helpful to read it as a group. Our lecturer Luisa pushed us to find the meaning in each sentence. This was not an easy task as there was a lot of information squashed into the first few pages. Luisa drew our attention to the fact that the text of the first chapter begins on the front cover. I have never seen this in a book design.



I made notes throughout the process of analysing the book:



I went away and watched the rest of the series on YouTube.com. (parts 1,2 &3)
Each episode expresses a different point.
Episode 1
- In the series- questioning the tradition of European painting (1400-1900) not focusing on the paintings themselves but the way we see them.
- A large part of seeing depends upon habit and convention.
- All the paintings of the tradition used the convention of perspective, which is unique to European art. Perspective centres everything on the eye of the beholder. Appearances travel into the eye. Perspective makes the eye the centre of the visible world, but the human eye can only be in one place at a time, it takes its visible world with it as it walks.
- The invention of the camera has changed not only what we see, but how we see it. The painting on the wall, like the human eye, can only be in one place at one time. The camera reproduces it, making it available in any size and anywhere, for any purpose.
- Venus and mars used to be a unique image, which it was only possible to see in the room where it was actually hanging. Now its image, or a detail of it can be seen in a million different places at the same time. As you look at the images now, your wallpaper is around them, your window is opposite them, your carpet is below them. At this same moment, they are on many screens, surrounded by different colours, different objects and different sounds. You are seeing them in the context of your own life. They are surrounded not by gilt frames, but by the familiarity of the room you are in and the people around you.
- The paintings are part of the history of the building it is in. for example, the church or chapel.
- Now the images come to you, you do not go to them. It is the image of the painting which travels now.
- The faces of paintings become messages. Pieces of information to be used, even used to persuade us to help purchase more originals, which these very reproductions have in many ways replaced.
- A reproduction does not have the same feeling of authenticity as the original artwork
- The pages of a book and a screen is never still. The lines are slightly moving. With a genuine original painting, there is a moment of stillness you have with the painting in a museum that cannot be replicated.
- Words you notice consciously. Music is subtler. It can work almost without you noticing it. However, music changes the meaning of a painting when it is played over the top. Words around it and music played over it changes the meaning of a painting.
- When paintings are reproduced, they have to hold their own against all the other information jostling around them to appear on the same page or the same screen.
- The meaning of an image can be changed according to what you see beside it or what comes after it.
- When you turn from one channel to another on television, this affects the next image you see on your screen. It alters the impact of an image in different ways.
- It means: reproductions of works of art can be used by anybody for their own purposes.
- Images can be used like words, we can talk with them. Reproduction should make it easier to connect our experience of art directly with other experiences.
- Reproductions make the paintings easily accessible, however the context they appear in can oppose this. The example Berger gives is the old paintings reproduced in an art book. The language used in the book, which surrounds the image, can inhibit the accessibility. Because of the use of difficult language. (mystification)
- Children connect images directly with their own experience.
- On television programmes, we receive images and meanings which have been arranged. Be skeptical of what a programme arranges for us to see.
Episode 2
- ‘Men dream of women, women dream of themselves being dreamt of.’ There is a focus on what women look like. They are looked at by men. How they look or how they should look. Behind every glance is a judgement. A woman is always accompanied by an image of herself
- The video switches between footage of working women in a lab, models, classical paintings of women and old and young women, plain and glamourous women.
- ‘From earliest childhood she is taught and persuaded to survey herself continually. She has to survey everything she is and everything she does because how she appears to others and particularly how she appears to men is of crucial importance for it is normally thought of as the success of her life.’
- In the average European oil painting, there were portraits of women as well as men but in one category, they were an ever occurring subject. That category was the nude. In the nudes of European painting, we can discover some of the criteria and conventions of which women were judged. We can see how women were seen.
- What is a nude?
- Different views on what a nude is: 1) to be without clothes- a form of art 2)to be naked is to be one’s self. To be nude is to be seen naked by others and yet not recognized for one’s self. A nude has to be seen as an object in order to be a nude.
- In the bible- Adam and Eve. The woman is blamed and punished by being made subservient to the man. In relation to the woman, the man becomes the agent of God. Moment of shame. It is the spectator’s looking which shames them (covering up with a leaf or hand)
- The nude implies an awareness of being seen by the spectator.
- Men looking at naked women and judging them is a theme in European art. They even call the women Vanity, thus repeating the story of Adam and Eve where the woman is blamed/shamed.
- ‘We are not discounting the role seeing plays in sexuality but there is a different between being seen as one’s self naked or seeing another in that way, and a body being put on display. To be naked is to be without disguise. To be on display is to have the surface of one’s own skin, the hairs of ones own body, turned into a disguise, a disguise which cannot be discarded.’
- It is possible to tell when the artist has actually seen the woman he has painted. There are not many examples if this in European art.
- Most of the nudes in oil paintings have been lined up and painted for the pleasure of the male spectator owner who will assess and judge them as sights. Their nudity is another form of dress . they are condemned to never being naked.
- ‘The painting is made to appeal to the sexuality of the male spectator, it has nothing to do with her sexuality. The convention of not painting the hair on a woman’s body helps towards the same end. Hair is associated with sexual power and passion. The women’s sexual passion needs to be minimized so that the spectator may feel he has the monopoly of such passion. The expressions on the women’s faces are responding with calculated charm to the man who she knows is looking at her although she doesn’t know him. The woman’s attention is directed at the spectator owner of the painting. Women are seldom shown dancing, they have to be shown languid, exhibiting a minimum energy. They are there to feed an appetite, not to have any of their own.’
- Absurdity! The only images we were seeing of women were them silent, mute.
- How men see women, or how they saw them in the past and how this influences how women see themselves today.
Berger asks women from the general public their thoughts about these paintings:
‘Paintings idealized and therefore unreal in any connection I might have of an image of myself. They don’t mean human beings to me.’
‘I compare myself to photographs more than paintings.’
‘Manet painting- the women aware of being humiliated.’
‘Women are always dressing as a part, to show the kind of character they want to be.’
‘Concept of availability = passivity. Opposite of action.’
‘Women’s sense of identity is based on what others think of them. But a man’s identity is based on his interaction with the world.’
Episode 3
- The beginning of the video shows footage of apples and fish at a market are interspersed with fish and apples in oil paintings. Playing over the top of the video is the sound from a modern day marketplace. Berger shows us people buying from the market. The exchange of money for these fresh products.
- ‘We buy, we consume, ours to give away, or more often, to keep.’
- The focus of the footage is not on the people’s faces or their identity, but on the act of handling goods, valuing them and buying them. Jewellery. Buying valuable objects.
- The most valuable object of all has become the oil painting. Oil paintings depict things. Buying the painting is almost like buying the object within the painting. Paintings often show treasures, but paintings have become treasures themselves
- A love of art= a sublime human experience
- What are these paintings? They are objects which can be bought and owned. Unique objects. A patron cannot be surrounded by music or poems as he can by pictures. They show him sights and many subjects. The only thing the paintings have in common : oil paints.
- The scenes that are depicted show wealth. Implicit in the wealth of European cultures, was the destruction of other cultures. But the Europeans believed their civilization was more advanced than any other.
- Paintings have symbolised wealth and power for centuries in different cultures, but they showed an order , European paintings showed a different kind of wealth. Their paintings glorified the ability to buy and furnish and to own.
- The paintings show the owner’s social status. Exaggerated claims. It is their clothes, not faces that dazzle. Oil paint allowed the subjects to be painted and look tangible. Privileged minority. Making a record of themselves.
- A painting gave the owner the pleasure of seeing themselves as the owner of their land.
- ‘The sight of it, makes us want to possess it.’ Publicity has taken the place of oil paintings in this way. (paintings were a place to show off our possessions)
Hella Jongerius
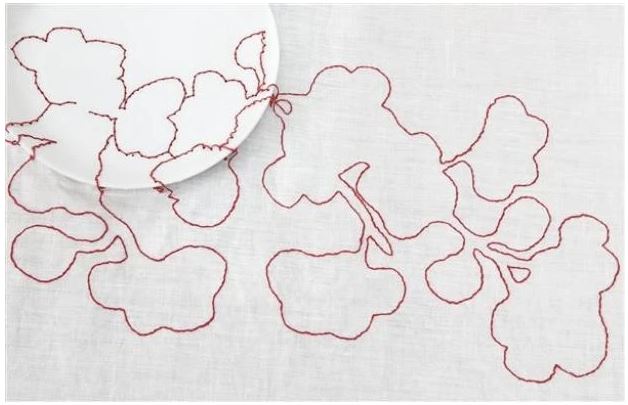
In class, we were shown 2 images and ask to write 100 words on each. I felt there was a connection between the 2 images, but did not guess that they were made by the same designer, Hella Jongerius. For the first image, I decided to write a creative response to the image. Luisa has told us that writing creatively and telling a story is part of a graphic designer’s skills. This piece was called Red Flower. When I first saw the image, I did not notice the plate until my classmate pointed it out. Then I saw the plate and the table as a setting for the artwork. I could not see how the stitches were attached to the plate. Only now, can I see the holes made in the plate to thread the thread through. (I could have got closer to the screen in the classroom and I may have been able to see the holes in the ceramic plate.)
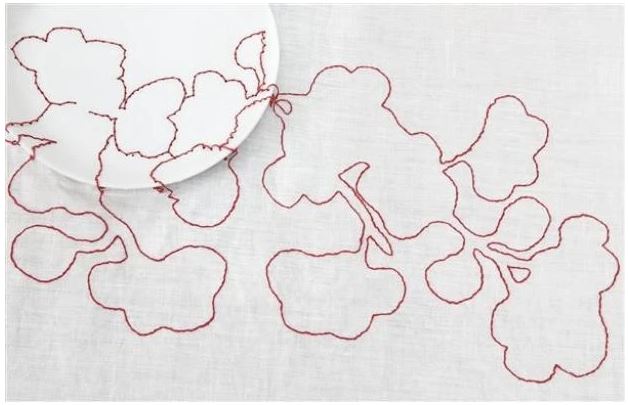

Hella Jongerius | Red Flower Embroidered Tablecloth (Circa 1999) | MutualArt
My response to the image:

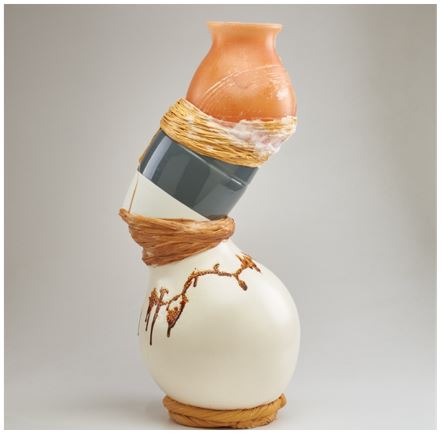
For the second image, we were asked to write about how it compares to the first. This image is called Stacked vase sculpture:


It was really interesting to hear my classmate’s views on the same images. I agreed with their points.

I quickly searched the designer and mainly looked at her other artworks. This helped me gain an understanding of the pieces we were shown and how they link.

At the end of the lecture, Luisa introduced us to the next brief, which is the presentation based on our chosen object. She explained that InDesign is a good programme to use for making presentation slides. I have only ever used Microsoft powerpoint, so this will be a new task for me. It was good to have an idea of what our aim is for the trip on Monday. This will help me to prepare, for example, I can take a sheet of questions written down to act as pointers to guide me. Going to London might be busy and hectic, so having these questions or bullet points can help me stay focused.
Looking at The Design Museum website helped us to get an idea of what to expect on our visit.


DESIGN MUSEUM POINTERS
- Relationship between form and function
- How it looks, what it is, your photos and other’s photos
- Use rich vocab: composition, layout, asymmetry, symmetry, organic, ephemeral, geometric, texture, luster, tactile quality
- Function- ergonomics, sometimes obvious, sometimes not, user friendly, does it communicate a message, is it entertaining? How does it do it?
- Context- history of the designer- where in the world? From a movement? When was it made?
- Was it successful for its purpose? Bear in mind when it was made. Did it discriminate people? Appropriate for design needs? Problematic? It may be successful in 1 aspect but problematic in another aspect.
- Emotional needs- functional but boring, emotionally dry, entertaining, environmental needs- 80s object may be disposable, toxic plastics, no thought for environmental problem.
- Gut reaction – what is your initial mood about the object?
- The presentation runs for 5 minutes. You will need to make it interesting and tell a story about your object, could be the story of you encountering the object. Take photos of the building.